does hardness testing get ultimate or yeild strength|strength vs toughness of materials : trader Two common measures are the ability to withstand a load without plastic deformation (yield strength) or without failure (ultimate strength). In the sketch below, Material 1 has higher strength than Material 2. WEBConheça a Biografia completa de Renato Cariani e inspire-se com esse grande campeão da vida e do esporte. O Sr. Renato Cariani nasceu em 1976, no bairro Cidade Dutra, na cidade de São Paulo, Estado de São .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web(TAP) Voruna drops to all fours and prepares 5 brutal charges that lock onto enemies. Ulfrun, the most powerful wolf, leads the attack as Voruna dashes toward her target. The pack deals increased damage to targets and nearby enemies that are inflicted by Status Effects. Lethal attacks double the damage of Voruna's remaining charges.
Yield Point Testing: Identifies the yield strength by observing when a material starts to deform plastically under stress. Hardness vs. Strength: Key Differences. Hardness is about a material’s resistance to surface deformation and wear, . No. There is no standard table for hardness to YS approximation. It would be better to determine the UTS from a standard table of hardness to ultimate tensile strength conversion .
Two common measures are the ability to withstand a load without plastic deformation (yield strength) or without failure (ultimate strength). In the sketch below, Material 1 has higher strength than Material 2. Therefore, another question is coming: does one-third of hardness represent the yield strength or ultimate tensile strength in all the materials? To further improve the . Hardness correlates only very loosely to yield strength and ductility, with high scatter (Figure 1). Hardness testing has many pitfalls that can lead to inaccurate .Ultimate strength refers to the maximum stress before failure occurs. Fracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occurs. Stiffness is how a component resists elastic deformation when a load is .
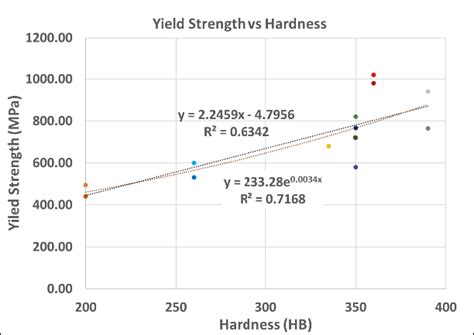
yield strength vs hardness
The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress.
how hard is the nc adjuser test
Both the yield strength and tensile strength of the steels exhibited a linear correlation with the hardness over the entire range of strength values. Empirical relationships are provided that. The material identification of steel concerns the determination of the main mechanical properties that affect the load-bearing capacity of structural elements or their .
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. Ultimate Tensile Strength of Aluminium. Ultimate tensile strength of Aluminium is 90 MPa (pure), 600 MPa (alloys). Material Strength. Strength is a measure of the stress a material can withstand. Two different measurements are used to define the strength of a material: The ultimate strength, which is the maximum stress the material . where S is the uniaxial flow strength and H is hardness. The factor c is termed as elastic constraint factor and has a value of approximately 3 for metals that do not strain harden appreciably when H is measured in kg f /mm .
AISI 304 Stainless Steel (UNS S30400, SS 304) AISI 304 stainless steel (UNS S30400) is the most widely used stainless steel, containing 18-20% Cr and 8-10.5% Ni, and also known as 18-8 stainless steel.SS 304 is non-magnetic under annealing conditions, but after cold working (such as stamping, stretching, bending, rolling), part of the austenite structure may be converted into .Conversion table/chart for Brinnel and Rockwell hardness scales and tensile strengths. Buy metals and plastics online in small quantities, cut to order. . then compares those to the approximate tensile strength that those scales indicate. Brinell Hardness: Rockwell Hardness: . FREE Mill Test Reports σ y = yield strength (F / A 0 at onset of plastic flow) σ 0.1% = 0.1% proof stress (F / A 0 at a permanent strain of 0.1%) (0.2% proof stress is often quoted instead; proof stress is useful for characterizing yield of a material that yields gradually, and does not show a distinct yield point) σ TS = tensile strength (F / A 0 at onset of necking) Following are the steps to measure yield strength: Standardized test specimens must be prepared in accordance with relevant standards or specifications as the first stage. . The term “yield point” refers to the upper and lower yield points, respectively. Ultimate stress point: This point denotes the highest stress a material can withstand .
Intuitively, most people have an understanding of hardness, even if they can’t provide a metallurgically correct definition. Most people have an idea of strength as well, although most non-technical people may not be aware that any given material has a number of different properties that fall under the category of strength (yield strength, tensile strength, .The ratio of yield strength to ultimate tensile strength is an important parameter for applications such steel for pipelines, . Hardness testing can therefore be an economical substitute for tensile testing, as well as providing local variations in yield strength due to, .Measuring the compressive strength of a steel drum. In mechanics, compressive strength (or compression strength) is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size (compression).It is opposed to tensile strength which withstands loads tending to elongate, resisting tension (being pulled apart). In the study of strength of materials, .
Strength = Ability of a material to withstand an applied load. There are several different measures of strength. Two common measures are the ability to withstand a load without plastic deformation (yield strength) or without failure (ultimate strength). In the sketch below, Material 1 has higher strength than Material 2.Strain energy. The area under the \(\sigma_e - \epsilon_e\) curve up to a given value of strain is the total mechanical energy per unit volume consumed by the material in straining it to that value.
• Offset yield strength • Ultimate Tensile strength, . Shear strength Yield point θ 12 Hardness • Brinell Hardness Test: 10mm diameter ball . 1000 or 3000kg • Rockwell Hardness Test: A cone shape indenter; the depth of penetration is measured. • Vickers Hardness Test: Pyramid shape indenter ()( 2 2 ) 2The height of the sections is equal to the average of the yield strength and the ultimate strength. The modulus of toughness can be approximated as: where S ty is the tensile yield strength, S tu is the tensile ultimate strength, ε y is the strain at yield, ε u is the ultimate strain (total strain at failure), and E is the elastic modulus.The yield strength is defined as the stress at which a predetermined amount of permanent deformation occurs. The graphical portion of the early stages of a tension test is used to evaluate yield strength. To find yield strength, the .Ultimate tensile strength. The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often .
Type 316L stainless steel density is 0.289 lb/in3 (8.0 g/cm3); melting point is 1375-1400 °C (2500-2550 °F); 0.2% yield strength is minimum 25 ksi (170 MPa) in annealed and hot finished condition, minimum 45 ksi (310 MPa) in annealed and cold finished condition; Minimum tensile strength is 70 ksi (485 MPa) in annealed and hot finished . Strength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design. Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and .
Ultimate Tensile Strength of Silver. Ultimate tensile strength of Silver is 110 MPa. Yield Strength of Silver. Yield strength of Silver is 45 MPa. Modulus of Elasticity of Silver. The Young’s modulus of elasticity of Silver is 45 MPa. The shear modulus of elasticity of Silver is 30 GPa. The bulk modulus of elasticity of Silver is 100 GPa.In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain.It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing).These curves reveal many of the properties of a material, such as the Young's .Ultimate Tensile Strength: 293 MPa: Yield Strength: 380 MPa: Young’s Modulus of Elasticity: 116 GPa: Brinell Hardness: 150 BHN: Melting Point: 1941 °C: Thermal Conductivity: 22 W/mK: Heat Capacity: . Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to .Ultimate Tensile Strength of Copper. Ultimate tensile strength of Copper is 210 MPa. Yield Strength of Copper. Yield strength of Copper is 33 MPa. Modulus of Elasticity of Copper. The Young’s modulus of elasticity of Copper is 33 MPa. The shear modulus of elasticity of Copper is 48 GPa. The bulk modulus of elasticity of Copper is 140 GPa.
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. Ultimate Tensile Strength of Beryllium. Ultimate tensile strength of Beryllium is 345 MPa. Yield Strength of BerylliumYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. Ultimate Tensile Strength of Titanium. Ultimate tensile strength of Titanium is 434 MPa, 293 MPa (pure). Yield Strength of Titanium
Introduction Definition of yield strength. Yield Strength: It is the yield limit of a metal material when it yields, i.e. the stress that resists slight plastic deformation. For metal materials without obvious yielding, the stress value that produces 0.2% residual deformation is specified as its yield limit, called the conditional yield limit or yield strength. This formula will give you the ultimate yield strength of that size and grade of bolt. Example: What is the ultimate yield strength of a 3/4″ diameter F1554 Grade 36 rod? This is the minimum requirement for F1554 grade 36. In other words, a 3/4″ diameter F1554 grade 36 anchor rod will be able to withstand 12,024 pounds force (lbf) without . First we will cover Hardness, Ultimate Tensile Strength, Elongation, Tensile Set, Young’s Modulus and Yield Strength. The results of these properties, except Hardness and Tensile Set, are from tension stress which is recorded on the stress-strain curve that is generated during a Ultimate Tensile Strength test.
O resultado do jogo do bicho de Goiás é divulgado cinco vez.
does hardness testing get ultimate or yeild strength|strength vs toughness of materials